Mobile Phone Technology
4G Mobile Network Architecture.
3G Mobile Network
image ©fromgentogen.usThe move to 4G LTE is a move to an Enhanced UTRAN architecture. The technology behind 4G is LTE standing for Long Term Evolution and the move to 4G was an evolution to the previous 3G network.
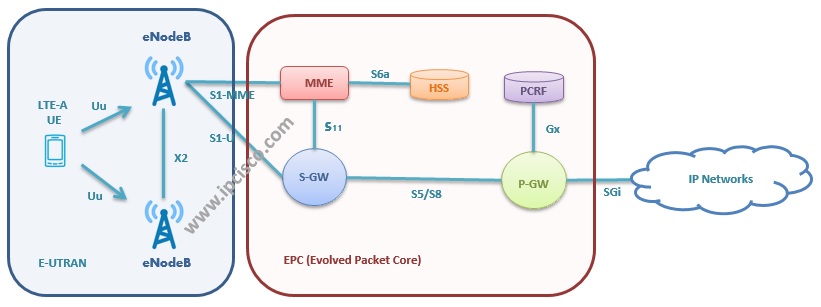
The 4G LTE or Enhanced UTRAN comprises :
- An enhannced Node B, which is the transceiver controlling the air interface that switches to the evolved Packet Core.
- The evolved packet core includes the serving gateway to control access to Packet Gateway or Packet Data Network.
- Managing the 4G network is the MME [Mobility Management Entity]. This is the core component in the 4G LTE architecture. It authenticates the mobile device and maintains the location of it thus taking over the role of the AUC [Authentication Centre] and VLR [Visitor Location Register] in 3G. A HSS [Home subscriber Servic]e provides the HLR [Home Location Register] functionality. Additionally the MME selects for the user equipment the correct SGW [Serving GateWay] to pass the data through. Pooling of MME resources can provide a more robust network.
- The MME can also switch the device to the 2G / GSM network if separate phone services are required. This happens if VoLTE is not available for the device at it's location.
© mobilephonetechnology.co.uk all rights reserved 2017-2026
